The Direct Variation Calculator is an essential tool for students, educators, and professionals in mathematics and sciences. This versatile calculator simplifies the process of solving direct variation problems by allowing users to input any two of the three key variables: the constant of variation, and the x or y values along a direct variation line. This calculator provides quick and accurate results. It’s an invaluable resource for exploring and understanding the principles of direct variation in algebra and its applications in real-world scenarios.
Direct Variation Calculator – Instantly Solve for k, x, or y in y = kx
Direct variation describes a simple relationship between two variables where one is a constant multiple of the other. This calculator makes it easy to determine the constant of variation or the value of one variable when the other is known, facilitating a deeper understanding of proportional relationships.
How to Use the Direct Variation Calculator
Using the Direct Variation Calculator is simple and intuitive:
- Enter Two of the Three Variables: Input any two of the following: constant of variation (k), x value, or y value. Leave the third variable blank.
- Calculate: Click the ‘Calculate’ button to find the missing variable.
- View Results: The calculated value of the missing variable will be displayed.
- Reset for New Calculations: Use the ‘Reset’ button to clear all fields for a new calculation.
Explanation of Direct Variation
Direct variation describes a relationship where two variables increase or decrease proportionally. The formula for direct variation is:
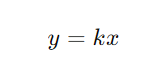
- k: The constant of variation
- x and y: The variables in direct proportion
Definition and Background of Direct Variation
Direct variation is a fundamental concept in algebra, illustrating how one variable changes in relation to another. It’s a linear relationship represented by a straight line passing through the origin in a coordinate plane, widely used in physics, economics, and engineering.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide for Direct Variation
- Identify the Known Variables: Start with two known values among k, x, and y.
- Input the Values: Enter these values in the respective fields of the calculator.
- Calculate the Unknown Variable: The calculator will compute the missing variable based on the direct variation formula.
Table of Example Calculations for Direct Variation
| Constant of Variation (k) | X Value | Y Value | Calculated Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5 | – | Y = 10 |
| – | 3 | 6 | k = 2 |
| 4 | – | 8 | X = 2 |
Glossary for Direct Variation
- Variable: A symbol representing a number in an equation or function.
- Proportionality: A relationship where one quantity varies directly as another.
- Linear Relationship: A relationship that forms a straight line when graphed.
FAQ Section
Q: What does the constant of variation represent? A: The constant of variation (k) represents the ratio between two variables in a direct variation relationship.
Q: Can the constant of variation be negative? A: Yes, a negative constant indicates an inverse relationship between the variables.
Q: Is direct variation always a linear relationship? A: Yes, in direct variation, the relationship between the two variables is always linear.



