The Enthalpy Calculator emerges as an essential tool in the field of thermochemistry, offering a seamless way to calculate the change in enthalpy of a reaction. This calculator is incredibly valuable for students, chemists, and engineers dealing with thermodynamic processes.
It computes the total change in enthalpy by considering the change in internal energy, volume, and pressure of a system. Additionally, it can determine changes in energy or volume when other values are known, making it a versatile instrument for various calculations in chemistry and physics.
How to Use the Enthalpy Change Calculator
- Input the Change in Internal Energy (ΔU): Enter the value in Joules. This represents the energy change in the system.
- Enter the Change in Volume (ΔV): Provide the volume change in cubic meters.
- Specify the Change in Pressure (ΔP): Input this value in Pascals.
- Calculate: Click on ‘Calculate Enthalpy Change‘ to obtain the result.
- Reset for New Calculation: Use the ‘Reset’ button to clear all inputs for a fresh calculation.
Understanding the Enthalpy Calculation Formula
The formula for calculating enthalpy change (ΔH) is:
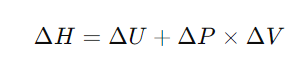
Where:

Definition and Background of Enthalpy Change Calculator
Enthalpy, a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the energy required to make space for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide for Enthalpy Change Calculator
- Gather the Data: Determine the changes in internal energy, volume, and pressure for the system.
- Input Values: For instance, if ΔU is 500 Joules, ΔV is 0.002 cubic meters, and ΔP is 100,000 Pascals (1 atm), input these values in the respective fields.
- Perform Calculation: Click ‘Calculate’. The calculator will show the enthalpy change, considering both energy and work done due to volume change.
Table of Example Calculations
| ΔU (Joules) | ΔV (m³) | ΔP (Pascals) | ΔH (Joules) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 0.002 | 100,000 | 700 |
| 1000 | 0.001 | 50,000 | 1050 |
| 1500 | 0.003 | 200,000 | 2100 |
Glossary for Enthalpy Change
- Enthalpy (H): A property of a thermodynamic system, equivalent to its internal energy plus the product of its pressure and volume.
- Internal Energy (U): The total energy contained within a system.
- Pressure (P): The force exerted per unit area.
- Volume (V): The amount of space occupied by a substance.
FAQ Section for Enthalpy Change Calculator
Q: What is the significance of enthalpy in chemical reactions? A: Enthalpy helps in understanding heat changes during chemical reactions, which is crucial for predicting reaction behavior and designing processes.
Q: Can enthalpy change be negative? A: Yes, a negative enthalpy change indicates an exothermic reaction where heat is released.
Q: How does enthalpy differ from entropy? A: Enthalpy is a measure of total energy, while entropy measures the degree of disorder or randomness in a system.
This comprehensive guide on the Enthalpy Calculator provides a practical tool for understanding and computing energy changes in thermodynamic systems, enhancing the grasp of concepts crucial in various scientific and engineering fields.

