The Average Atomic Mass Calculator is a vital tool for students, researchers, and professionals in chemistry and physics. This calculator simplifies the process of determining the average atomic mass of an element, which represents the weighted average of the masses of its isotopes, based on their natural abundance.
Average Atomic Mass Calculator – Instantly Compute Weighted Atomic Mass from Isotopes
Our team converts drinks into code — fuel us to build more free tools!
By inputting the percentage abundance and mass of up to five different isotopes, you can quickly calculate the average atomic mass, enhancing understanding of atomic structure and facilitating accurate chemical calculations.
How to Use the Average Atomic Mass Calculator
- Enter Isotope Data: Input the mass and percentage abundance of each isotope. You can add up to 5 isotopes.
- Add More Isotopes: Click ‘Add Isotope’ to include additional isotopes.
- Calculate: After entering all data, click ‘Calculate’ to obtain the average atomic mass.
- Reset: Use ‘Reset’ to clear all fields and start a new calculation.
Understand the Average Atomic Mass Formula
The Average Atomic Mass Calculator employs the formula:
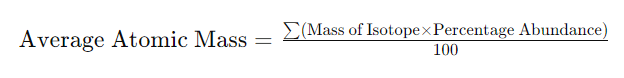
This formula considers the mass of each isotope and its relative abundance, providing a weighted average that reflects the most common atomic mass an element would exhibit in nature.
The Significance of Average Atomic Mass
Average atomic mass is a crucial concept in chemistry, representing the average mass of an element’s isotopes as they naturally occur. This measurement is fundamental in understanding atomic structures, calculating molecular weights, and performing various chemical analyses and experiments.
The concept of average atomic mass is central in the field of chemistry and has wide-ranging implications and uses. Let’s explore this topic in more detail:
What is the Atomic Scale
Average vs. Individual Atomic Masses: Unlike individual atomic masses, which are specific to each isotope, the average atomic mass takes into account the relative abundance of each isotope in nature. This makes it a more practical and realistic representation of the elements as they are found in nature.
Reflection of Isotopic Composition: The average atomic mass is a reflection of the isotopic composition of an element in a given sample, which can vary slightly depending on the source. For example, terrestrial and extraterrestrial samples of the same element might have slightly different average atomic masses due to variations in isotopic composition.
Applications of Average Atomic Mass in Various Fields
Chemical Calculations: In stoichiometry, the average atomic mass is used to calculate the molar mass of compounds, which is essential for determining the proportions of elements in chemical reactions.
Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry: These analytical techniques rely heavily on the concept of average atomic mass for the identification and quantification of substances. The isotopic patterns observed in mass spectrometry are directly related to the average atomic masses of the elements involved.
Pharmaceuticals and Medicine: Accurate knowledge of atomic masses is crucial in the design and synthesis of pharmaceuticals. In nuclear medicine, isotopes are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, and their effectiveness can depend on their atomic mass.
Educational Importance
Fundamental Chemistry Education: The concept of average atomic mass is taught early in chemistry education, laying the foundation for more advanced topics like molecular biology, pharmacology, and environmental science.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills: Working with average atomic mass calculations helps students develop analytical and quantitative skills, which are essential in scientific research and practical applications.
Implications of Average Atomic Mass in Research and Industry
- Material Sciences: In the development of new materials, particularly alloys and polymers, understanding the atomic mass of constituent elements is crucial for predicting and tailoring properties like strength, conductivity, and reactivity.
- Environmental Studies: In studying environmental samples, the average atomic mass of elements can provide insights into the source and history of pollutants, aiding in environmental protection and remediation efforts.
- Astrophysics and Geology: The average atomic mass of elements can offer clues about the processes involved in the formation of the Earth and other celestial bodies, contributing to our understanding of the universe.
In summary, the concept of average atomic mass is not just a basic chemical notion but a fundamental tool across various scientific disciplines. Its relevance extends from the classroom, where it forms a core part of chemistry education, to advanced research in fields as diverse as environmental science, material science, and astrophysics.
The ability to accurately measure and understand average atomic masses allows scientists and researchers to make predictions, perform accurate calculations, and develop new technologies and solutions across a broad spectrum of industries.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide for Average Atomic Mass Calculator
- Gather Isotope Information: Identify the isotopes of the element and their respective masses and natural abundances.
- Input the Data: Enter this information into the calculator.
- Calculate: Click the ‘Calculate’ button to view the average atomic mass.
- Reset and Repeat: For new calculations, use the ‘Reset’ button.
Examples Table for Average Atomic Mass
This table provides an overview of isotopes for two elements, Chlorine and Carbon, including their atomic masses, natural abundances, and the calculated average atomic mass for each element.
| Element | Isotope 1 (Mass, Abundance) | Isotope 2 (Mass, Abundance) | Average Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorine | 35 amu, 75% | 37 amu, 25% | 35.5 amu |
| Carbon | 12 amu, 98.93% | 13 amu, 1.07% | 12.01 amu |
Let’s break down the table to understand it thoroughly below.
Elements of Table for Average Atomic Mass:
- Chlorine
- Carbon
Isotopes:
Each element has different isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (having the same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons. This results in different atomic masses.
Chlorine:
- Isotope 1: Chlorine-35 (35 amu, 75%)
- Isotope 2: Chlorine-37 (37 amu, 25%)
Carbon:
- Isotope 1: Carbon-12 (12 amu, 98.93%)
- Isotope 2: Carbon-13 (13 amu, 1.07%)
Atomic Mass Unit (amu):
The atomic mass unit is a standard unit of mass that quantifies mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom, which is approximately equal to 1.66 × 10^-27 kilograms.
Abundance:
Abundance refers to the percentage of each isotope found naturally. For example, 75% of Chlorine in nature is Chlorine-35, and 25% is Chlorine-37.
Average Atomic Mass:
The average atomic mass of an element is calculated by taking the weighted average of the atomic masses of its naturally occurring isotopes. The weight here refers to the abundance of each isotope.
Calculations:
For Chlorine:
- (35 amu × 75%) + (37 amu × 25%) = 26.25 amu + 9.25 amu = 35.5 amu
For Carbon:
- (12 amu × 98.93%) + (13 amu × 1.07%) ≈ 11.87 amu + 0.14 amu = 12.01 amu
Interpretation:
- Chlorine: The average atomic mass of Chlorine is closer to 35 amu than 37 amu because the more abundant isotope (Chlorine-35) influences the average more significantly.
- Carbon: The average atomic mass of Carbon is slightly above 12 amu because of the small contribution of Carbon-13 to the average.
In summary, this table illustrates how the natural abundance of isotopes influences the average atomic mass of elements. It’s a fundamental concept in chemistry, particularly in isotopic chemistry and mass spectrometry, and is crucial for understanding the composition of elements as found in nature.
Glossary for Average Atomic Mass
- Isotope: Variants of a chemical element, differing in neutron number but having the same atomic number.
- Atomic Mass: The mass of a single atom, typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu).
- Abundance: The relative occurrence of an isotope in nature, usually expressed as a percentage.
FAQ Section for Average Atomic Mass Calculator
Q: What is the importance of average atomic mass in chemistry? A: Average atomic mass is vital for understanding the properties of elements, calculating molecular weights, and conducting precise chemical reactions.
Q: Can the Average Atomic Mass Calculator be used for all elements? A: Yes, as long as you have accurate mass and abundance data for the element’s isotopes.
Q: Why does the average atomic mass often appear as a decimal? A: The average atomic mass is a weighted average based on isotopic abundance, which often results in a decimal value rather than a whole number.
Utilize the Average Atomic Mass Calculator for an efficient, accurate approach to understanding and working with elemental isotopes, enhancing your comprehension and capabilities in the fascinating field of chemistry.
Additional Online Resources about Average Atomic Mass Calculator
To deepen your understanding of isotopes and average atomic mass, here are some useful resources:
- Chemistry LibreTexts – Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass: This source provides a detailed explanation of isotopes, atomic mass, and the calculation of average atomic mass. It explains that the atomic mass of an element as shown in the periodic table is a weighted average mass of all its isotopes present in a naturally occurring sample. The calculation of the average atomic mass involves multiplying each isotope’s mass by its fractional abundance and summing these values. The example of boron is used to illustrate the calculation, and the concept is expanded with exercises and examples for different elements Chemistry LibreTexts.
- Chemistry LibreTexts – Calculating Average Atomic Mass: This section offers a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the average atomic mass of elements, emphasizing the importance of understanding the percent natural abundance of each isotope. It includes examples and exercises that guide you through the process of calculating the average atomic mass using the isotopic mass and natural abundance Chemistry LibreTexts.
- Wikipedia – Isotope: This comprehensive entry explains the concept of isotopes, their properties, and the difference between isotopes and nuclides. It describes how isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but differ in the number of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers. The entry also discusses the historical background of the term ‘isotope’ and provides examples of isotopes for various elements, such as carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 Wikipedia.
- AACT – Simulation Activity: Isotopes & Calculating Average Atomic Mass: This educational resource offers a simulation activity designed to help students understand atomic structure, isotopes, and average atomic mass. It includes a tutorial and practice exercises where students can calculate the average atomic mass for various elements based on their isotopic composition. The simulation aims to provide a practical and interactive approach to learning these concepts AACT.
These resources collectively offer a comprehensive understanding of isotopes, their role in determining the atomic mass of elements, and how the average atomic mass is calculated based on isotopic abundance.



