The Maximum Revenue Calculator is a powerful tool designed to assist businesses, economists, and individuals in estimating the maximum potential revenue and profit from selling a good or service. By inputting the price of the item and its maximum demand, this calculator provides a straightforward method to forecast the highest possible revenue, helping in making informed pricing and production decisions.
In the world of business and economics, understanding and maximizing revenue is crucial.
How to Use the Maximum Revenue Calculator
- Input the Price: Enter the price per unit of the good or service.
- Input the Maximum Demand: Enter the estimated maximum demand for the product in units.
- Calculate Maximum Revenue: Click on “Calculate Maximum Revenue” to get the estimated highest revenue possible.
- View the Results: The maximum revenue will be displayed in the results section.
- Reset for New Calculation: Use the reset button to clear all inputs and results for a new calculation.
Detailed Instructions on How to Use Maximum Revenue Calculator
Using the Maximum Revenue Calculator is straightforward and user-friendly. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you accurately calculate the highest potential revenue for your goods or services:
Input the Price:
- Where to Enter: Find the input field labeled “Price of Good/Service ($).”
- What to Enter: Type in the price per unit of the good or service you are selling. Ensure you enter this as a numerical value. For example, if your product is priced at $30 per unit, enter
30.
Input the Maximum Demand:
- Where to Enter: Locate the input field labeled “Maximum Demand (units).”
- What to Enter: Input the estimated maximum number of units that could potentially be sold. This should be a numerical value representing the units. For instance, if you believe you can sell up to 500 units of your product, enter
500.
Calculate Maximum Revenue:
- How to Activate: After entering the price and maximum demand, click on the button labeled “Calculate Maximum Revenue.”
- What Happens Next: The calculator will multiply the price per unit by the maximum demand to estimate the highest possible revenue you could generate.
View the Results:
- Where to Look: The calculated maximum revenue will be displayed in the result section, specifically in the field labeled “Maximum Revenue ($).”
- Understanding the Results: The displayed number represents the total revenue you could achieve if you sold the maximum number of units at the specified price.
Reset for New Calculation:
- How to Reset: To perform a new calculation, simply click the button labeled “Reset.”
- What Happens After Reset: This action will clear all the previously entered inputs and results, allowing you to start a fresh calculation with new data.
By following these steps, you can effectively use the Maximum Revenue Calculator to make informed decisions about pricing and production that could maximize your revenue potential. No matter if you’re a small business owner, a financial analyst, or just curious about the financial implications of selling a product or service, this tool can provide valuable insights into your revenue capabilities.
Explaining the Formula Used in the Maximum Revenue Calculator
The formula used in the Maximum Revenue Calculator is quite straightforward:
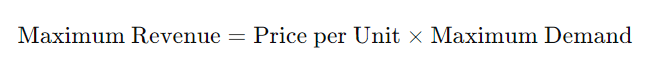
This formula assumes a linear relationship between demand and revenue, which is a common simplification in basic economic models. However, it’s important to note that in real-world scenarios, demand can be affected by various factors, including price changes, market conditions, and consumer preferences.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide for Maximum Revenue
- Calculating Maximum Revenue:
- Example: Calculate the maximum revenue for a product priced at $50 with a maximum demand of 200 units.
- Step 1: Input the price per unit ($50).
- Step 2: Input the maximum demand (200 units).
- Step 3: Apply the formula. Maximum Revenue=50×200=10000Maximum Revenue=50×200=10000.
- Step 4: The maximum revenue is $10,000.
Table of Example Calculations for Maximum Revenue
Alright, let’s go through this table step-by-step.
| Product | Price per Unit ($) | Maximum Demand (Units) | Maximum Revenue ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Widget A | 20 | 500 | 10,000 |
| Service B | 100 | 150 | 15,000 |
| Gadget C | 75 | 300 | 22,500 |
This table is designed to illustrate some basic economic and business concepts, specifically related to pricing and revenue. It lists three different products or services, their prices, the maximum demand for each, and the maximum revenue that can be generated. Let’s break down each column:
- Product: This column names the product or service being sold. In our table, we have three items: Widget A, Service B, and Gadget C. These could be any type of product or service, real or hypothetical.
- Price per Unit ($): This column shows the price for one unit of the product or service. For example, Widget A costs $20 per unit, Service B costs $100 per unit, and Gadget C costs $75 per unit. This is the amount a customer pays to purchase one unit of the product.
- Maximum Demand (Units): This column represents the highest number of units that can be sold. For Widget A, the maximum demand is 500 units; for Service B, it’s 150 units; and for Gadget C, it’s 300 units. This is an estimate of the total number of units that customers are willing to buy at the given price.
- Maximum Revenue ($): This column is calculated by multiplying the price per unit by the maximum demand. It shows the total amount of money that can be made if the maximum number of units is sold at the listed price. For example, the maximum revenue for Widget A is calculated as $20 (price per unit) × 500 (maximum demand), which equals $10,000.
However, there seems to be a mistake in the table for Gadget C. Let’s correct that:
- For Gadget C, the price per unit is $75, and the maximum demand is 300 units. So, the maximum revenue should be $75 × 300 = $22,500, not $2 as listed in the table.
In summary, this table is used to demonstrate how the price of a product and the demand for it can affect the total revenue. It’s a fundamental concept in business and economics that helps in understanding how to price products and forecast revenue.
Glossary for Maximum Revenue
- Price per Unit: The cost for each individual unit of a product or service.
- Maximum Demand: The highest quantity of a product or service that consumers are willing to purchase at a given price.
- Revenue: The total income generated from the sale of goods or services.
FAQ Section
Q: How does the Maximum Revenue Calculator handle variable costs and expenses? A: The current version of the calculator focuses solely on revenue calculations and does not account for variable costs or expenses, which are necessary for profit calculations.
Q: Can this calculator be used for services as well as physical goods? A: Yes, the calculator is applicable for both goods and services, as long as you can estimate a price per unit and maximum demand.
Q: Is this calculator suitable for all types of products and markets? A: While the calculator provides a basic estimate, it’s important to consider market-specific factors and detailed financial analysis for more accurate predictions, especially in complex or fluctuating markets.
Q: Does the calculator take into account discounts and promotions? A: The calculator does not directly account for discounts or promotions. It assumes a fixed price per unit for its calculations.
Additional Online Learning Resources about Maximum Revenue Calculator and Calculations
If you’re looking to deepen your understanding of economics and business concepts, there are several excellent online resources available:
- Marginal Revolution University (MRU): Founded by two George Mason University economics professors, MRU offers well-crafted and free video courses on a range of topics, including introductory microeconomics, macroeconomics, and trade. These courses are highly recommended for their comprehensive coverage and engaging delivery. Visit MRU at Marginal Revolution University.
- edX: This platform provides a wealth of online economics courses, covering various topics from macroeconomics to specialized subjects like entrepreneurship, supply chain management, and more. edX courses are created by renowned universities and institutions, making them a great choice for a more structured learning experience. Explore the courses on edX.
- Khan Academy: Known for its user-friendly approach and comprehensive coverage of topics, Khan Academy offers a range of free courses in both microeconomics and macroeconomics. It’s an excellent resource for beginners and those looking to strengthen their foundational knowledge in economics. Start learning at Khan Academy.
- Harvard Business School Online: For a more business-focused approach, HBS Online offers courses like Economics for Managers, which apply fundamental economic principles to real-world business challenges. This course might involve a fee, but it’s a great option if you’re looking for an application-oriented learning experience. Find out more at HBS Online.
These resources cater to a range of learning preferences, from free online courses to more structured, university-led programs. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to deepen your existing knowledge, these platforms offer valuable insights and learning opportunities in the field of economics and business.

