The Resultant Force Calculator is designed for physics students, engineers, and professionals dealing with dynamics and statics. It enables users to input up to five different forces along with their respective angles or directions, and calculates the resultant force acting on an object.
Resultant Force Calculator – Instantly Find the Magnitude & Direction of Combined Forces
Our team converts drinks into code — fuel us to build more free tools!
This calculator is particularly useful for analyzing complex systems where multiple forces are at play, simplifying the process of vector addition and providing accurate results essential for problem-solving and design in physics and engineering. Calculating the resultant force of two or more forces can be a crucial task in various fields such as physics, engineering, and mechanics. The Resultant Force Calculator simplifies this process by allowing you to determine the net force resulting from two forces acting at different angles.
Report an issue
Spotted a wrong result, broken field, or typo? Tell us below and we’ll fix it fast.
Formula for Resultant Force Calculator:
To calculate the resultant force, you can use the following formula: Resultant Force (R) = √[(F₁ cos(θ₁) + F₂ cos(θ₂))^2 + (F₁ sin(θ₁) + F₂ sin(θ₂))^2] Where:
- R is the resultant force.
- F₁ and F₂ are the magnitudes of the two forces.
- θ₁ and θ₂ are the angles at which the forces are applied.
Explanation of the Resultant Force Calculation
The calculator uses vector addition to compute the resultant force. The formulae are:
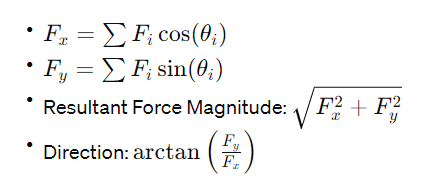
How to Use the Simplified Resultant Force Calculator
To utilize the Resultant Force Calculator, follow these steps:
- Enter the Forces and Angles: Input the magnitude of up to five forces in Newtons (N) and their respective angles in degrees.
- Calculate Resultant Force: Click the ‘Calculate Resultant Force’ button to evaluate the overall force.
- View Results: The calculator displays the resultant force magnitude in Newtons and its direction in degrees.
- Reset for New Calculations: To perform a new calculation or correct an input, use the ‘Reset’ button.
How to Use Advanced Resultant Force Calculator:
- Enter the magnitude of the first force (F₁) in newtons (N).
- Input the angle at which the first force is applied (θ₁) in degrees.
- Enter the magnitude of the second force (F₂) in newtons (N).
- Input the angle at which the second force is applied (θ₂) in degrees.
- Click the “Calculate” button to determine the resultant force.
Example: Suppose you have a 30 N force acting at an angle of 45 degrees and a 40 N force acting at an angle of 60 degrees. Using the Resultant Force Calculator, you can find the net force resulting from these two forces.
Definition and Background of Resultant Force
Resultant force is the single force which represents the vector sum of multiple forces acting on an object. It determines the object’s motion and is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the study of dynamics.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide for Resultant Force
- Identify Individual Forces: List all forces acting on the object, including their magnitudes and directions.
- Input Data: Enter each force’s magnitude and direction into the calculator.
- Calculate and Interpret: The calculator will provide the magnitude and direction of the resultant force, indicating the object’s motion.
Table of Example Calculations for Resultant Force
| Force 1 (N) | Angle 1 (degrees) | Force 2 (N) | Angle 2 (degrees) | Resultant Force (N) | Direction (degrees) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0 | 5 | 90 | 11.18 | 26.57 |
| 20 | 45 | 10 | 180 | 17.07 | 112.62 |
| 15 | 30 | 10 | 270 | 17.92 | 326.31 |
Glossary for Resultant Force
- Vector Addition: The process of adding two or more vectors.
- Magnitude: The size or amount of a vector.
- Angle of Direction: The angle a vector makes with a reference direction.
FAQs:
- What is the resultant force?
- The resultant force is the net force obtained when two or more forces act on an object. It represents the combined effect of these forces.
- Why is it essential to calculate the resultant force?
- Calculating the resultant force helps determine the overall effect of multiple forces, which is crucial in analyzing the motion and stability of objects.
- What are the units of resultant force?
- The resultant force is typically measured in newtons (N) in the International System of Units (SI).
- What happens if the resultant force is zero?
- If the resultant force is zero, the object will be in equilibrium, meaning it will not accelerate or change its state of motion.
- Can the resultant force be greater than the sum of the individual forces?
- Yes, the resultant force can be greater than the sum of the individual forces when they act at different angles, causing constructive interference.
- What if I don’t know the angles of the forces?
- You must know the angles of the forces to calculate the resultant force accurately. Use a protractor or other measurement tools to determine the angles.
- Is this calculator suitable for three or more forces?
- No, this calculator is designed for two forces. For more than two forces, you’ll need to use vector addition methods.
- Can I use this calculator for non-right angles?
- Yes, this calculator works for any angles, not just right angles. Ensure you enter the angles in degrees.
Conclusion:
The Resultant Force Calculator simplifies the process of finding the net force resulting from two forces acting at different angles. Whether you’re studying physics, engineering, or any field that deals with forces, this tool can help you quickly and accurately determine the resultant force, enabling you to make informed decisions and predictions in your work.



