Calculating wholesale prices is an essential task for businesses that sell products in bulk. To simplify this process, we have created a Wholesale Price Calculator. This calculator will help you determine the wholesale price of your products based on the cost price, markup percentage, and the quantity you plan to sell.
Wholesale Price Calculator – Instantly Find Your Profitable Wholesale Price
Our team converts drinks into code — fuel us to build more free tools!
Report an issue
Spotted a wrong result, broken field, or typo? Tell us below and we’ll fix it fast.
Formula used in Wholesale Price Calculator
The formula for calculating the wholesale price is straightforward:
Wholesale Price = Cost Price + (Cost Price x (Markup Percentage / 100))
How to Use Wholesale Price Calculator?
- Enter the Cost Price of your product. This is the price at which you purchased or manufactured the item.
- Next, input the Markup Percentage you want to apply to the cost price. This percentage represents the profit margin you wish to achieve.
- Specify the Quantity of products you intend to sell in bulk.
- Click the “Calculate” button to get the total Wholesale Price.
Example of a Calculation with Wholesale Price Calculator
Suppose you bought a product for $10, and you want to apply a 20% markup. You plan to sell 50 of these products in bulk. Here’s how to use the calculator:
- Cost Price: $10
- Markup Percentage: 20%
- Quantity: 50
After clicking “Calculate,” you’ll get the Wholesale Price of $600.
- Use our CPR Calculator
Table with Examples of Various Wholesale Price Calculations
Below is a simple table with examples of various wholesale price calculations. Feel free to use this Wholesale Price Calculation table for your study, research or seminars.
| Item | Cost Price ($) | Markup Percentage (%) | Quantity | Wholesale Price Calculation | Total Wholesale Price ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 20 | 50 | 10 + (10 * 20/100) | 600 |
| B | 15 | 30 | 30 | 15 + (15 * 30/100) | 585 |
| C | 8 | 25 | 40 | 8 + (8 * 25/100) | 400 |
| D | 12 | 15 | 60 | 12 + (12 * 15/100) | 828 |
| E | 20 | 10 | 100 | 20 + (20 * 10/100) | 2200 |
Explanation of the Table:
- Item: The product identifier.
- Cost Price ($): The cost at which the item was purchased or manufactured.
- Markup Percentage (%): The percentage of profit margin added to the cost price.
- Quantity: The number of items to be sold in bulk.
- Wholesale Price Calculation: The formula used to calculate the price of a single item.
- Total Wholesale Price ($): The total wholesale price for the quantity (single item price multiplied by the quantity).
In-depth explanation of the Wholesale Price Calculation Table
The provided table serves as a practical guide to understanding the calculation of wholesale prices. It illustrates how different variables — cost price, markup percentage, and quantity — interact to determine the final wholesale price of products. This table is designed to aid businesses in visualizing and planning their pricing strategy for bulk sales.
Here’s another Wholesale Price Calculator table with real-life examples of wholesale price calculations. This table includes various types of products that a business might typically deal with, along with practical figures for cost price, markup percentage, and quantity.
The resulting wholesale price calculations demonstrate how businesses might price these items for bulk sales.
| Product Type | Cost Price ($) | Markup Percentage (%) | Quantity | Wholesale Price Calculation | Total Wholesale Price ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic T-Shirts | 12 | 25 | 100 | 12 + (12 * 25/100) = $15 | 1500 |
| Handmade Candles | 5 | 40 | 200 | 5 + (5 * 40/100) = $7 | 1400 |
| Eco-Friendly Bags | 8 | 30 | 150 | 8 + (8 * 30/100) = $10.40 | 1560 |
| Specialty Coffee | 3 | 50 | 300 | 3 + (3 * 50/100) = $4.50 | 1350 |
| Tech Accessories | 20 | 20 | 50 | 20 + (20 * 20/100) = $24 | 1200 |
| Gourmet Chocolates | 10 | 35 | 80 | 10 + (10 * 35/100) = $13.50 | 1080 |
| Natural Cosmetics | 15 | 25 | 120 | 15 + (15 * 25/100) = $18.75 | 2250 |
| Craft Beer Packs | 18 | 30 | 60 | 18 + (18 * 30/100) = $23.40 | 1404 |
| Artisanal Bread | 2 | 50 | 200 | 2 + (2 * 50/100) = $3 | 600 |
| Fitness Equipment | 50 | 15 | 40 | 50 + (50 * 15/100) = $57.50 | 2300 |
Explanation of the Table:
- Product Type: A variety of products that businesses might sell, ranging from clothing to food items and tech accessories.
- Cost Price ($): The initial cost to produce or acquire the product.
- Markup Percentage (%): The desired profit margin added to the cost price.
- Quantity: The number of units intended for sale in bulk.
- Wholesale Price Calculation: The formula used to calculate the wholesale price per unit.
- Total Wholesale Price ($): The total revenue expected from selling the bulk quantity at the calculated wholesale price.
This table is designed to provide a realistic perspective on how different types of products might be priced in a wholesale context, reflecting various market scenarios and business strategies.
Breaking Down the Table’s Components
- Item: Each row represents a different product (Item A, B, C, etc.), providing a diverse set of examples. This variety helps in understanding how the calculation applies across different pricing scenarios.
- Cost Price: The cost price reflects the initial expense incurred to obtain or produce each product. This figure is critical as it forms the base upon which markup is added. It’s a direct reflection of production or acquisition costs and is crucial for accurate pricing.
- Markup Percentage: This percentage is indicative of the profit margin the business aims to achieve on top of the cost price. The markup percentage can vary depending on factors like market competitiveness, product type, and business objectives. It’s a strategic figure that determines how much above the cost price the product should be sold to achieve desired profits.
- Quantity: The quantity column shows the number of items intended for sale in bulk. This quantity factor is essential for calculating the total wholesale price for the batch, an important figure for inventory and sales planning.
- Wholesale Price Calculation: This column provides the formula used for each item, combining the cost price and markup percentage. It simplifies how each unit’s wholesale price is derived, offering a clear view of the pricing structure.
- Total Wholesale Price: Finally, the total wholesale price multiplies the individual item’s wholesale price by the quantity. This total is what the business would receive from selling the bulk quantity at the calculated wholesale price.
Significance of the Wholesale Price Calculation Table in Business Planning
The table is more than just a collection of numbers; it’s a strategic tool for businesses. By understanding and applying these calculations, businesses can set wholesale prices that cover costs, ensure profitability, and remain competitive in the market. It aids in making informed decisions about pricing strategies, ultimately impacting the business’s bottom line.
Moreover, the table format allows for easy adaptation to different products and scenarios, making it a versatile tool for various business models. Whether you are a small startup or a larger enterprise, this table can be a cornerstone in developing a robust pricing strategy for your wholesale operations.
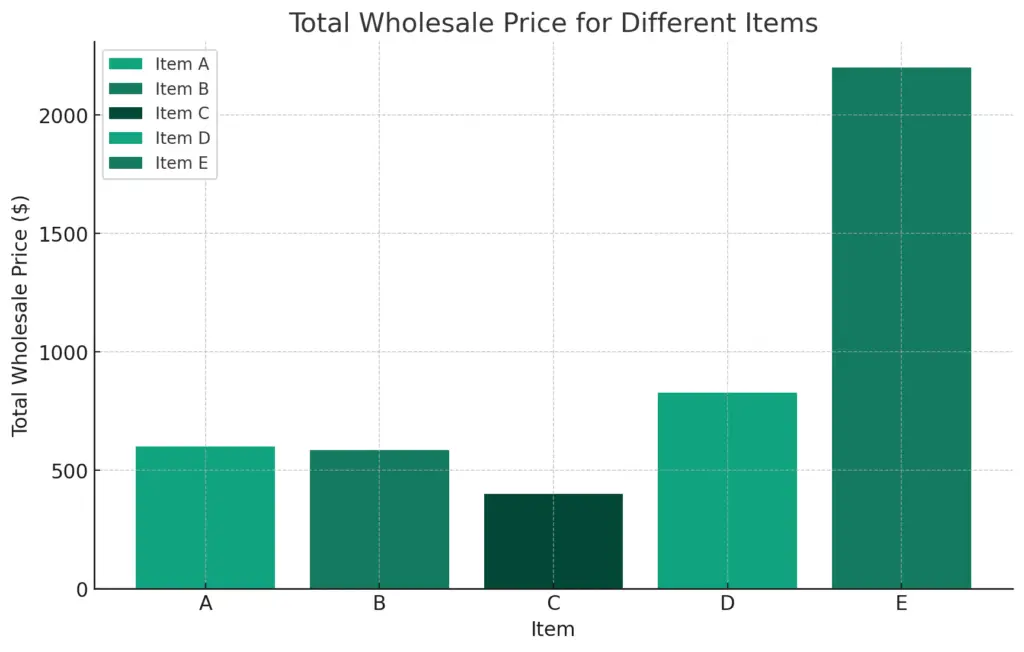
The chart above visualizes the total wholesale prices for different items, as detailed in the provided table. Each bar represents an item (A, B, C, D, E), with the height indicating the total wholesale price for the specified quantity of that item.
This visualization helps in quickly grasping how varying cost prices, markup percentages, and quantities impact the total wholesale value of different products. Such a chart can be particularly useful for comparing the profitability and pricing strategies across a range of products in a straightforward and visually engaging manner.
Understand Markup Percentages within Wholesale Price Calculator Topic
Understanding and effectively setting markup percentages is a vital aspect of wholesale pricing strategy. It requires a blend of market awareness, competitive analysis, and strategic planning.
Tools like the Wholesale Price Calculator empower businesses to make these crucial decisions with confidence and agility, ensuring that their pricing strategies not only drive profit but also align with market dynamics.
By figuring out the skill of markup percentages, businesses can secure a competitive edge in the bustling wholesale marketplace.
Determining the Right Markup for Competitive Advantage
When it comes to setting wholesale prices, one of the most critical factors is understanding and applying the right markup percentage. This not only affects your profit margins but also plays a significant role in positioning your product competitively in the market.
The Wholesale Price Calculator is an invaluable tool in this regard, assisting businesses in making strategic pricing decisions that balance profitability with market competitiveness.
Markup Percentage: The Balancing Act
The markup percentage is essentially your profit margin. It is the difference between the cost price of your product and its selling price. Deciding on the right markup percentage is a strategic decision that requires careful consideration of various factors, such as production costs, market demand, and competitor pricing. A too-high markup might lead to overpricing your product out of the market, while a too-low markup might not cover costs or yield sufficient profit.
Industry Standards and Market Research
To optimize your markup percentage, it’s important to understand industry standards. Different industries have different average markups, influenced by factors like product type, market saturation, and customer expectations.
Conducting thorough market research can provide insights into what competitors are charging and what customers are willing to pay, helping you to set a markup percentage that ensures competitiveness and profitability.
Using the Wholesale Price Calculator Effectively
The Wholesale Price Calculator simplifies this process. By inputting your cost price and experimenting with different markup percentages, you can instantly see how changes affect your wholesale price.
This can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to find the sweet spot in their pricing strategy, ensuring that their products remain attractive to bulk buyers while maintaining a healthy profit margin.
Adapting to Market Changes
In today’s dynamic market, flexibility in pricing strategies is key. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your markup percentage in response to market changes, cost fluctuations, or competitive actions can help maintain market relevance and profitability.
The Wholesale Price Calculator becomes an essential tool in this ongoing process, enabling quick recalculations and informed decision-making.
Key Influencers in Your Wholesale Pricing Strategy
Skill of calculating a wholesale pricing means understanding and responding to market trends, competitive actions, supply chain dynamics, and customer demand. It’s a complex but rewarding challenge.
To help you achieve that, use tools like the Wholesale Price Calculator. It equips you to make informed, agile decisions, setting you up for sustained success in the competitive world of wholesale trade.
Staying Ahead in a Dynamic Market
As a business professional in the wholesale industry, recognizing the factors that impact your pricing is crucial for your success. You’re navigating a landscape shaped by various external forces – from the ever-changing market trends to the strategies of your competitors, and from the ebb and flow of supply chain costs to the evolving demands of your customers.
Tools like the Wholesale Price Calculator aren’t just about setting prices; they’re about giving you the power to adapt and thrive in these conditions.
Market Trends: Your Pricing Compass
Market trends are your compass in the wholesale world. They reflect everything from shifts in consumer preferences to broader economic conditions and industry-specific changes. Keeping your finger on the pulse of these trends is vital. It informs you of what customers are willing to pay and sets the stage for how the market values products.
Whether it’s capitalizing on a high-demand trend with a higher markup or navigating a saturated market, understanding these trends is key.
Competitor Pricing: Know Your Field
In the competitive arena of wholesale, understanding how your rivals price their products is essential. It’s not always about matching or undercutting their prices. Sometimes, it’s about differentiating your product as a premium choice.
What’s important is to strategically position your pricing in a way that reflects your product’s value while keeping an eye on the competition.
Supply Chain Fluctuations: The Cost Factor
Your supply chain is the lifeline of your cost structure. Variations in the costs of raw materials, transportation, and production can directly influence your pricing.
A deep dive into your supply chain helps anticipate these changes, ensuring your pricing strategy remains both competitive and profitable, even in turbulent times.
Customer Demand in the Context of Wholesale Prices
Your customers are your ultimate guide. Their demand dictates how you price your products. Factors influencing this demand can range from seasonal shifts to broader market and economic trends.
High demand can give you the leverage for higher prices, while lower demand might require more strategic pricing to move your inventory.
Leverage Tools for Strategic Adaptation
Incorporating these factors into your pricing strategy is critical, and that’s where the Wholesale Price Calculator comes into play. It allows you to adjust swiftly to changing costs, market conditions, and competitive landscapes. This agility is your key to maintaining profitability and relevance in the dynamic wholesale market.
Industry Standards and Market Research: A Scientific Approach to Wholesale Pricing
Defining and calculating optimal wholesale prices is a task that benefits greatly from a scientific and research-oriented approach.
By understanding industry standards through data analysis and conducting comprehensive market research, you can set markup percentages that are both competitive and profitable.
Remember, the wholesale pricing strategy is not a one-time calculation but an ongoing process of adaptation and refinement, much like the scientific process itself.
The Scientific Edge in Pricing
In the world of wholesale pricing, adopting a scientific and research-driven approach can provide a significant competitive edge.
Understanding industry standards and conducting thorough market research are not just business activities; they are akin to scientific explorations that require meticulous attention to detail, analysis, and understanding of complex market dynamics.
As a scientist and researcher in this field, you must dive deep into the data and trends that drive pricing decisions.
Decoding Industry Standards: A Data-Driven Perspective
Each industry operates with its own set of unwritten rules and benchmarks, including average markups. These standards are influenced by various factors such as the type of product, the level of market saturation, and customer expectations.
To optimize your markup percentage, a data-driven approach is essential. Analyzing historical pricing data, industry reports, and financial statements of competitors can reveal patterns and benchmarks in pricing.
The Role of Market Research
Market research is the backbone of informed pricing strategies. It goes beyond just understanding what competitors charge. It involves delving into customer behavior, preferences, and willingness to pay.
This can be approached through quantitative methods like surveys and pricing experiments, or qualitative methods like focus groups and customer interviews. The objective is to gather data that reflects the real-world scenario of how your product is perceived and valued in the market.
Integrating Research into Wholesale Pricing
Armed with this research and data, you can now approach the task of setting or adjusting wholesale prices with a scientific lens. It’s about finding that sweet spot where your product is priced competitively yet profitably.
Use tools like the Wholesale Price Calculator not just as a calculator but as a tool for applying your research findings. Input different markup percentages based on your research and observe how they impact the final price and your competitive position.
Adapting to Evolving Standards and Research Findings
Remember, industry standards and market preferences are not static. They evolve with changes in technology, economic conditions, and consumer trends.
Continuously updating your research and adapting your pricing strategy is crucial. It’s a process of constant learning, analyzing, and applying – much like any scientific endeavor.
Benefits of Using a Wholesale Price Calculator
The benefits of using a Wholesale Price Calculator are clear and impactful. It brings simplicity, accuracy, and strategic depth to the pricing process, factors that are critical in the competitive world of wholesale business.
By leveraging this tool, businesses can ensure their pricing strategies are not only effective and profitable but also resilient in the face of an ever-evolving market landscape.
Simplifying the Complexity of Pricing
In the intricate world of wholesale business, the Wholesale Price Calculator emerges as an indispensable tool. Its primary advantage lies in simplifying complex pricing calculations, a task that can be both time-consuming and prone to errors when done manually. This tool streamlines the process, allowing you to focus more on strategic aspects of your business rather than getting bogged down in numbers.
Ensuring Accuracy in Calculations
Accuracy in pricing is not just important – it’s crucial. Even small errors in calculation can lead to significant losses over time, especially when dealing with large quantities typical in wholesale transactions.
The Wholesale Price Calculator eliminates these risks by providing precise calculations. This precision ensures that your pricing strategy is based on reliable data, thereby protecting your profit margins. (wine price estimate)
Facilitating Strategic Decision-Making
One of the key advantages of the Wholesale Price Calculator is its role in aiding strategic decision-making. By quickly adjusting variables like cost price, markup percentage, and quantity, you can immediately see the impact on your wholesale price.
This ability to simulate different scenarios helps in making informed decisions about pricing strategies, ensuring they are aligned with market conditions and business objectives.
Adapting to Market Changes
The business landscape is ever-changing, and adaptability is key to survival and success. The Wholesale Price Calculator allows for quick recalculations in response to market changes such as shifts in supply costs, competitor pricing adjustments, or changes in customer demand.
This agility is vital in maintaining a competitive edge and responding proactively to market dynamics.
Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
Efficiency and productivity are significantly enhanced by using a Wholesale Price Calculator. It reduces the time and effort required for pricing calculations, freeing up resources that can be better utilized in other areas of your business, like marketing, customer service, or product development.
Wholesale vs. Retail Pricing: Key Differences
The distinction between wholesale and retail pricing is more than just a matter of different numbers. It’s about understanding the different market dynamics, cost structures, and customer expectations in each sector.
By mastering these nuances, businesses can make informed decisions about their pricing structures, ensuring they maximize their profitability and market potential in both wholesale and retail environments.
Navigating Two Distinct Pricing Strategies
For businesses involved in both wholesale and retail sectors, comprehending the differences between wholesale and retail pricing is crucial.
Each sector requires a unique approach and strategy, and understanding these differences can significantly influence your overall profitability and market positioning.
Wholesale Pricing: The Volume Game
Wholesale pricing is fundamentally about selling products in bulk quantities, typically to retailers or other businesses who then sell to the end consumer. The key here is volume.
Because you’re selling large quantities, the per-unit profit margin is often lower compared to retail pricing. However, the overall profit is made on the volume sold.
The pricing strategy in wholesale is influenced by factors like production costs, market demand, and competition, but it also heavily depends on the operational efficiencies and the ability to maintain a low cost of goods sold.
Retail Pricing: Maximizing Per-Unit Profit
Retail pricing, on the other hand, focuses on selling products directly to the end consumer. Here, the pricing strategy is more about maximizing the profit on each individual sale. Retail prices are generally higher than wholesale prices to cover additional costs such as retail staff, store upkeep, and marketing efforts.
Retail pricing also considers the perceived value of the product to the consumer, competitor pricing, and the willingness of consumers to pay.
The Impact of Pricing Structures on Profitability
Understanding these pricing structures is vital for businesses operating in both arenas. The wholesale price must be set in a way that allows retailers to add their markup and still offer a competitive retail price.
On the flip side, retailers need to understand the wholesale price to set a retail price that ensures profitability while remaining attractive to consumers.
Adapting Strategies for Market Success
The challenge for businesses is to balance these two pricing strategies effectively. This balancing act involves understanding the market you’re operating in, the nature of your products, and the expectations of your customers, both wholesale and retail.
Tools like the Wholesale Price Calculator can aid wholesalers in setting prices that are competitive yet profitable, taking into account the need for an appealing price point for retailers.
Real-World Examples of Wholesale vs. Retail Pricing with Wholesale Price Calculator
The examples below illustrate how businesses across different industries manage the delicate balance between wholesale and retail pricing.
They highlight the need to understand the market and customer expectations in both segments to set prices that ensure profitability while remaining competitive and attractive to end consumers.
Example 1: Fashion Apparel Company
A fashion apparel company manufactures a line of jeans. For wholesale, they price each pair at $30, targeting retailers who will sell them to consumers. The retailers, after factoring in costs like store rent, staff salaries, and marketing, sell the jeans for $80 per pair.
Here, the wholesale price needs to be low enough for the retailer to add a substantial markup, while still keeping the retail price attractive and competitive in the consumer market.
Example 2: Electronics Manufacturer
An electronics manufacturer produces a new line of headphones. They set the wholesale price at $50 per unit for bulk orders to electronic retail chains. (romi calculate the)
These retail chains then sell the headphones for $120 each, covering their higher operating costs and aiming for a higher per-unit profit. The pricing reflects the added value of customer service, immediate product availability, and post-purchase support offered by the retailers.
Example 3: Local Organic Food Producer
A local organic food producer sells boxes of organic vegetables to both supermarkets (wholesale) and directly to consumers at a farmers’ market (retail). They price the box at $15 for supermarkets, who then sell it for $25.
At the farmers’ market, the same box is priced at $20, reflecting the direct relationship with consumers, lower overhead costs compared to supermarkets, and the perceived value of buying directly from the producer.
Example 4: Specialty Coffee Roaster
A specialty coffee roaster offers their beans at a wholesale price of $10 per pound to cafes and $18 per pound to individual customers at their own retail outlet. The cafes price the coffee at $20 per pound, considering their ambiance, customer service, and location. (quilt cost estimate)
The roaster’s retail outlet also adds value through customer education about coffee varieties and brewing techniques, justifying the higher retail price compared to the wholesale rate.
Example 5: Pharmaceutical Products Distributor
A pharmaceutical products distributor sells medications to pharmacies at a wholesale rate, which is significantly lower than the retail price set by pharmacies.
For instance, a medication might be sold at a wholesale price of $15 per unit to pharmacies, which then sell it to customers for $45 per unit. The retail pricing reflects additional costs such as pharmacy operations, expert advice from pharmacists, and convenience for the customer.
Integration with Business Management Tools: Enhancing Efficiency and Streamlining Operations
The integration of the Wholesale Price Calculator with other business management tools represents a forward-thinking approach to business operations.
In today’s competitive market, this integration is not just about keeping up with technology; it’s about leveraging it to gain a strategic advantage. Businesses that embrace this integration are positioning themselves for greater efficiency, accuracy, and profitability in the long run. (revshare revenue share)
The Convergence of Technology and Business Efficiency
In the contemporary, tech-driven business landscape, the integration of tools like the Wholesale Price Calculator with other business management systems is not just a convenience; it’s a necessity for operational efficiency and strategic decision-making. This integration represents a significant step towards a more streamlined, data-driven approach to business management.
Seamless Integration: The Key to Streamlined Operations
Connecting with Inventory Management Systems: Integrating the Wholesale Price Calculator with inventory management systems can dramatically improve efficiency. This connection allows for real-time tracking of stock levels and costs, directly feeding into the calculation of wholesale prices. It ensures that pricing decisions are based on the most current inventory data, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
Enhanced Financial Reporting with Accounting Software: Linking the calculator with accounting software can automate the process of recording financial transactions. When you update wholesale prices, these changes can automatically reflect in your financial statements and reports. This integration provides a more accurate and up-to-date view of your business’s financial health, aiding in better financial planning and analysis.
CRM Systems for Customer-Centric Pricing Strategies: By integrating with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, businesses can leverage customer data and purchasing history to make more informed pricing decisions. This integration can help in understanding customer behavior and preferences, allowing for pricing strategies that are better aligned with customer expectations and market trends.
E-Commerce Platforms for Dynamic Pricing: For businesses selling online, integrating the Wholesale Price Calculator with e-commerce platforms can enable dynamic pricing capabilities. This means that wholesale prices can be adjusted in real-time based on various triggers such as changes in demand, competitor pricing, or inventory levels.
Supply Chain Management for Cost-Effective Pricing: Linking the calculator with supply chain management tools can provide insights into logistics costs, supplier pricing, and lead times. This information is critical for setting wholesale prices that are competitive yet profitable, taking into account the entire supply chain ecosystem.
The Benefits of Integration: More Than Just Time-Saving
Data Accuracy and Consistency: Integrated systems ensure that data across various platforms is consistent and up-to-date, reducing the risk of errors.
Improved Decision-Making: Access to comprehensive, real-time data allows for more informed and strategic decision-making.
Operational Efficiency: Automating data transfer between systems saves time and reduces manual efforts, allowing staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Better pricing strategies and efficient operations ultimately lead to a better customer experience, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
FAQs
Q: What is the Cost Price?
A: The Cost Price is the original price at which you purchased or manufactured a product.
Q: What is the Markup Percentage?
A: The Markup Percentage is the profit margin you want to add to the Cost Price. It’s usually expressed as a percentage of the Cost Price.
Q: Why is it essential to calculate Wholesale Prices?
A: Calculating Wholesale Prices is crucial for businesses to ensure profitability and set competitive prices when selling products in bulk.
Q: Can I use this calculator for any product type?
A: Yes, you can use this calculator for various product types, whether you sell physical goods or services in bulk.
Q: Is the Markup Percentage always based on the Cost Price?
A: Yes, the Markup Percentage is typically calculated based on the Cost Price to determine the Wholesale Price.
Q: Can I use decimals for the Cost Price and Markup Percentage?
A: Yes, you can use decimal values for more precise calculations.
Q: Is the Quantity limited when using this calculator?
A: No, you can input any quantity you want to calculate the total Wholesale Price.
Q: What does “readonly” mean in the Wholesale Price input field?
A: The “readonly” attribute makes the Wholesale Price field uneditable, ensuring that the calculated value cannot be modified.
Conclusion
The Wholesale Price Calculator simplifies the process of determining the wholesale price of your products. By entering the Cost Price, Markup Percentage, and Quantity, you can quickly calculate the total Wholesale Price, helping you make informed business decisions.
Sources and Literature:
For comprehensive information on wholesale and retail pricing strategies, you can refer to several websites that offer detailed insights and guidelines. These sources provide valuable information ranging from how to calculate prices effectively to understanding market dynamics that affect pricing decisions.
- Shopify’s Guide on Pricing Wholesale & Retail Products (2024): Shopify offers an extensive guide on pricing strategies for both wholesale and retail products. It includes mathematical formulas for determining a product’s price, margin, markup, and profitability. This resource is particularly helpful for retailers who sell products both directly to consumers and in a wholesale manner. For more details, visit their website.
- Metrobi’s Ultimate Guide for Retailers (2024): Metrobi provides a comprehensive breakdown of wholesale vs. retail pricing, including key differences and factors influencing retail prices. It covers various components that contribute to the final retail price and explains how market trends, operating costs, and customer perception influence pricing strategies. For a deeper understanding, check their guide.
- Product Distribution Strategy’s Take on Wholesale and Retail Pricing: This site offers a practical viewpoint on why pricing strategy is essential in both wholesale and retail contexts. It explains the impact of factors like operating expenses, shipping, and storage on pricing, and offers insights into optimizing retail prices for profitability and market positioning. For more insights, you can read their article.
- McKinsey’s Insights on Pricing in Retail: McKinsey provides a detailed analysis of pricing strategies in retail, highlighting how digital trends are reshaping retail pricing. It discusses the importance of understanding customer price perception and leveraging data for pricing strategies. To explore these insights further, visit McKinsey’s page.
- BlueCart’s Comparison of Wholesale vs. Retail Price: This source delves into the nuances between wholesale and retail pricing, discussing factors like consumer perception, market price, and product novelty. It emphasizes the importance of a value-based pricing model that accounts for buyer demographics and consumer trends. For a thorough exploration, visit BlueCart.
Each of these websites provides a unique perspective on pricing strategies in the wholesale and retail sectors, offering valuable information for businesses looking to optimize their pricing models and strategies. (percentage and discount)



